Weight and Cardiovascular Disease

What is overweight and obesity?
Overweight and obesity are terms to describe high body weight and body fat. Overweight and obesity can be measured by the Body Mass Index (BMI) which is a calculation based on weight in relation to height.
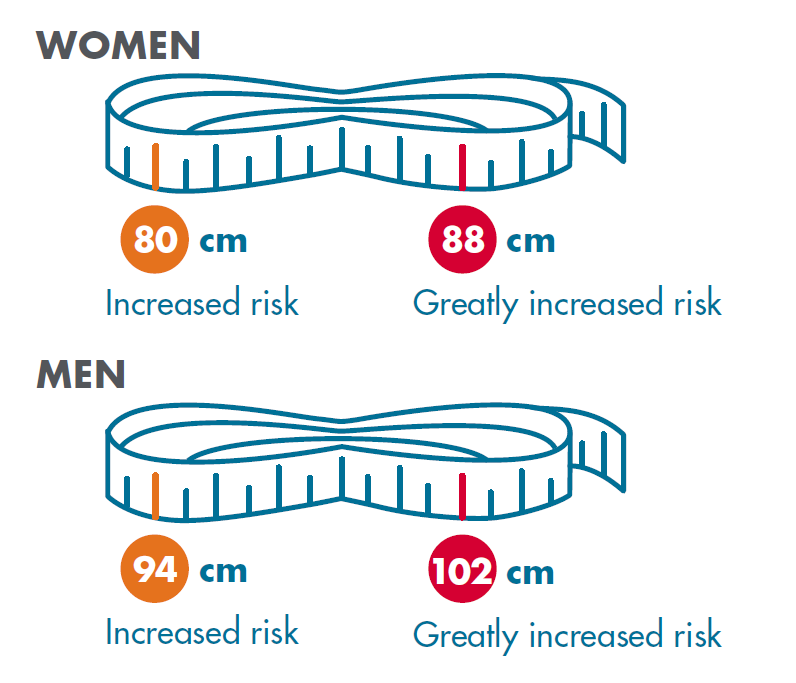
Waist circumference is also important as it tells us how much fat is around our internal organs. The fat around our internal organs, known as ‘visceral fat’, can be harmful to health if our bodies have a lot of it. Visceral fat releases harmful chemicals and hormones into our bloodstream which can damage cells. This is why visceral fat is referred to as “toxic fat”.
Living with overweight, obesity, or higher waist circumference increases the risk of developing chronic diseases including some cancers, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes. It also increases the risk of developing other health issues, including high blood pressure, gall bladder disease, fertility problems, lower back pain and sleep apnoea. The more excess weight or fat a person is carrying, the higher their risk of health issues.
What is cardiovascular disease?
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a term used to describe all diseases and conditions involving the heart and blood vessels. In Australia, the main types of cardiovascular diseases are coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
What causes cardiovascular disease?
Cardiovascular disease is more common as we get older, and is also influenced by our genes. The following factors also increase your risk of CVD:
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Poor diet including low intake of fruit and veg and high intake of saturated fat and salt
- Physical inactivity
- Carrying excess body fat
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
How does excess weight increase the risk of CVD?
Carrying excess body fat, particularly if it’s stored around the waist and vital organs increases the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, and this risk increases the higher BMI gets.
Excess body fat places direct stress on the heart and blood vessels, and may advance metabolic conditions which worsen cardiovascular disease. Poor diet and physical inactivity also increase the risk of high blood pressure and high blood cholesterol, which are major risk factors for coronary heart disease and stroke. As blood pressure and blood cholesterol levels get closer to the normal range, risk of cardiovascular disease decreases.

What can I do to reduce my risk of cardiovascular disease?
The best things you can do to achieve or maintain a healthy body weight to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes are to eat a variety of healthy foods based on the Australian Dietary Guidelines, and to participate in exercise or physical activity every day.
These things will improve your health and reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes, whether or not your weight or waist circumference changes.
For personalised advice, we encourage you to see your local GP who may refer you to an Accredited Practising Dietitian. If you’re after more information, useful websites include Eat for Health, Heart Foundation, Cancer Council and Diabetes Australia.